Arithmetic Sequence Formula
If you wish to find any term (also known as the [latex]{{nth}}[/latex] term) in the arithmetic sequence, the arithmetic sequence formula should help you to do so. The critical step is to be able to identify or extract known values from the problem that will eventually be substituted into the formula itself.
When you’re done with this lesson, you may check out my other lesson about the Arithmetic Series Formula.
Let’s start by examining the essential parts of the arithmetic sequence formula:
Parts of the Arithmetic Sequence Formula
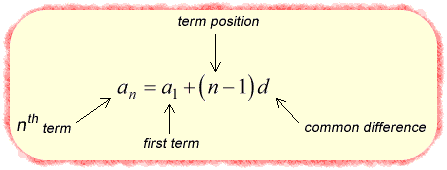
Where:
[latex]\large{a_n}[/latex] = the term that you want to find
[latex]\large{a_1}[/latex] = first term in the sequence
[latex]\large{n}[/latex] = the term position (ex: for 5th term, n = 5 )
[latex]\large{d}[/latex] = common difference of any pair of consecutive or adjacent numbers
Let’s put this formula in action!
Examples of How to Apply the Arithmetic Sequence Formula
Example 1: Find the 35th term in the arithmetic sequence 3, 9, 15, 21, …
There are three things needed in order to find the 35th term using the formula:
- the first term ( [latex]{a_1}[/latex])
- the common difference between consecutive terms ([latex]d[/latex])
- and the term position ([latex]n[/latex] )
From the given sequence, we can easily read off the first term and common difference. In a nutshell, the common difference is the constant difference between any pair of adjacent terms.The term position is just the [latex]n[/latex] value in the [latex]{n^{th}}[/latex] term, thus in the [latex]{35^{th}}[/latex] term, [latex]n=35[/latex].
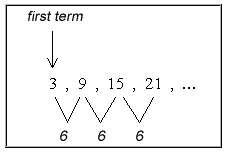
Therefore, the known values that we will substitute in the arithmetic formula are
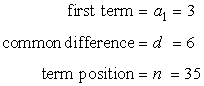
So the solution to finding the missing term is,

Therefore, the 35th term of the arithmetic sequence is [latex]207[/latex].
Example 2: Find the 125th term in the arithmetic sequence 4, −1, −6, −11, …
This arithmetic sequence has the first term [latex]{a_1} = 4[/latex], and a common difference of −5.
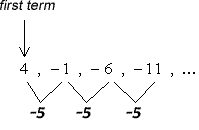
Since we want to find the 125th term, the [latex]n[/latex] value would be [latex]n=125[/latex]. The following are the known values we will plug into the formula:
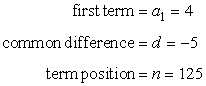
The missing term in the sequence is calculated as,
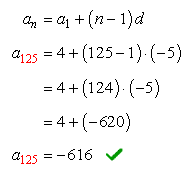
Therefore, the 125th term of the arithmetic sequence is [latex]-616[/latex].
Example 3: If one term in the arithmetic sequence is [latex]{a_{21}} = – 17[/latex] and the common difference is [latex]d = – 3[/latex]. Find the following:
a) Write a rule that can find any term in the sequence.
b) Find the twelfth term ( [latex]{a_{12}}[/latex] ) and eighty-second term ( [latex]{a_{82}}[/latex] ) term.
Solution to part a)
Because we know a term in the sequence which is [latex]{a_{21}} = – 17[/latex] and the common difference [latex]d = – 3[/latex], the only missing value in the formula which we can easily solve is the first term, [latex]{a_1}[/latex].
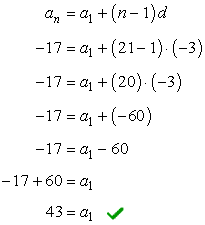
Since we found [latex]{a_1} = 43[/latex] and we know [latex]d = – 3[/latex], the rule to find any term in the sequence is
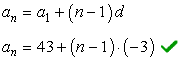
How do we really know if the rule is correct? What I would do is verify it with the given information in the problem that [latex]{a_{21}} = – 17[/latex].
So we ask ourselves, what is [latex]{a_{21}} = ?[/latex]
We already know the answer though but we want to see if the rule would give us −17.
Since [latex]{a_1} = 43[/latex], [latex]n=21[/latex] and [latex]d = – 3[/latex], we substitute these values into the formula then simplify.
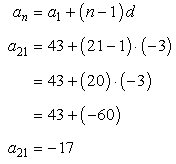
Which it does! Great.
Solution to part b)
To answer the second part of the problem, use the rule that we found in part a) which is
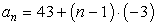
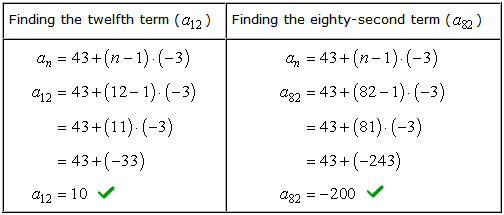
Here are the calculations side-by-side.
Example 4: Given two terms in the arithmetic sequence, [latex]{a_5} = – 8[/latex] and [latex]{a_{25}} = 72[/latex];
a) Write a rule that can find any term in the sequence.
b) Find the 100th term ( [latex]{a_{100}}[/latex] ).
Solution to part a)
The problem tells us that there is an arithmetic sequence with two known terms which are [latex]{a_5} = – 8[/latex] and [latex]{a_{25}} = 72[/latex]. The first step is to use the information of each term and substitute its value in the arithmetic formula. We have two terms so we will do it twice.
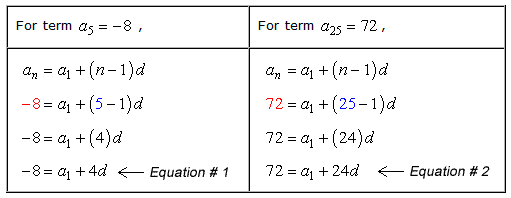
This is wonderful because we have two equations and two unknown variables. We can solve this system of linear equations either by the Substitution Method or Elimination Method. You should agree that the Elimination Method is the better choice for this.
Place the two equations on top of each other while aligning the similar terms.
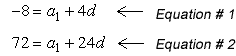
We can eliminate the term [latex]{a_1}[/latex] by multiplying Equation # 1 by the number −1 and adding them together.
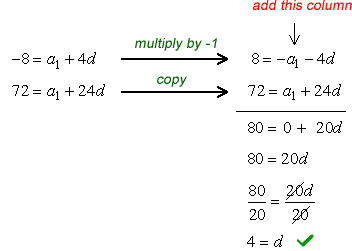
Since we already know the value of one of the two missing unknowns which is [latex]d = 4[/latex], it is now easy to find the other value. We can find the value of [latex]{a_1}[/latex] by substituting the value of [latex]d[/latex] on any of the two equations. For this, let’s use Equation #1.
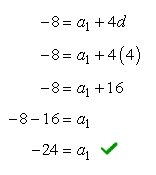
After knowing the values of both the first term ( [latex]{a_1}[/latex] ) and the common difference ( [latex]d[/latex] ), we can finally write the general formula of the sequence.
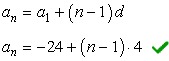
Solution to part b)
To find the 100th term ( [latex]{a_{100}}[/latex] ) of the sequence, use the formula found in part a)
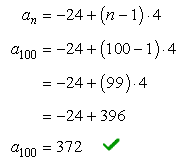
You may also be interested in these related math lessons or tutorials:
Definition and Basic Examples of Arithmetic Sequence
